Top 5 Cybersecurity Challenges for Financial Institutions in 2025
Discover the most critical cybersecurity threats facing banks and financial institutions in 2025, from AI-powered attacks to supply chain vulnerabilities, with practical mitigation strategies.

Introduction
The Evolving Cybersecurity Landscape in Banking
Financial institutions process over $5 trillion in daily transactions globally, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. According to recent industry reports, 72% of financial organizations experienced increased cyber risks in 2024, with attacks becoming more sophisticated and frequent.
Alarming Statistics
The median ransomware payment reached $200,000 in 2024, while infostealer attacks surged by 58%. Financial institutions face over 3,500 cyber attacks per week on average.
Challenge #1: Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and State-Sponsored Attacks
Nation-state actors and organized crime groups are launching sophisticated, long-term attacks against financial institutions. These APTs often remain undetected for months, gathering intelligence and mapping network infrastructures before executing major breaches.
- Multi-stage infiltration: Attackers establish persistent access through multiple entry points
- Living-off-the-land techniques: Using legitimate system tools to avoid detection
- Supply chain compromises: Targeting third-party vendors to reach primary targets
- Zero-day exploits: Leveraging unknown vulnerabilities in critical systems
import psutil
import hashlib
import time
from datetime import datetime
def monitor_unusual_processes():
"""Monitor for suspicious process patterns"""
baseline_processes = set()
while True:
current_processes = set()
for proc in psutil.process_iter(['pid', 'name', 'cmdline']):
try:
process_signature = f"{proc.info['name']}:{' '.join(proc.info['cmdline'])}"
current_processes.add(hashlib.md5(process_signature.encode()).hexdigest())
except (psutil.NoSuchProcess, psutil.AccessDenied):
continue
# Detect new processes
new_processes = current_processes - baseline_processes
if new_processes and baseline_processes:
print(f"[{datetime.now()}] Alert: {len(new_processes)} new processes detected")
baseline_processes = current_processes
time.sleep(60) # Check every minuteChallenge #2: Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and Double Extortion
The ransomware landscape has evolved into a service-based model, making attacks more accessible to low-skill criminals. Modern ransomware groups employ double and triple extortion tactics, encrypting data while threatening to leak sensitive customer information.
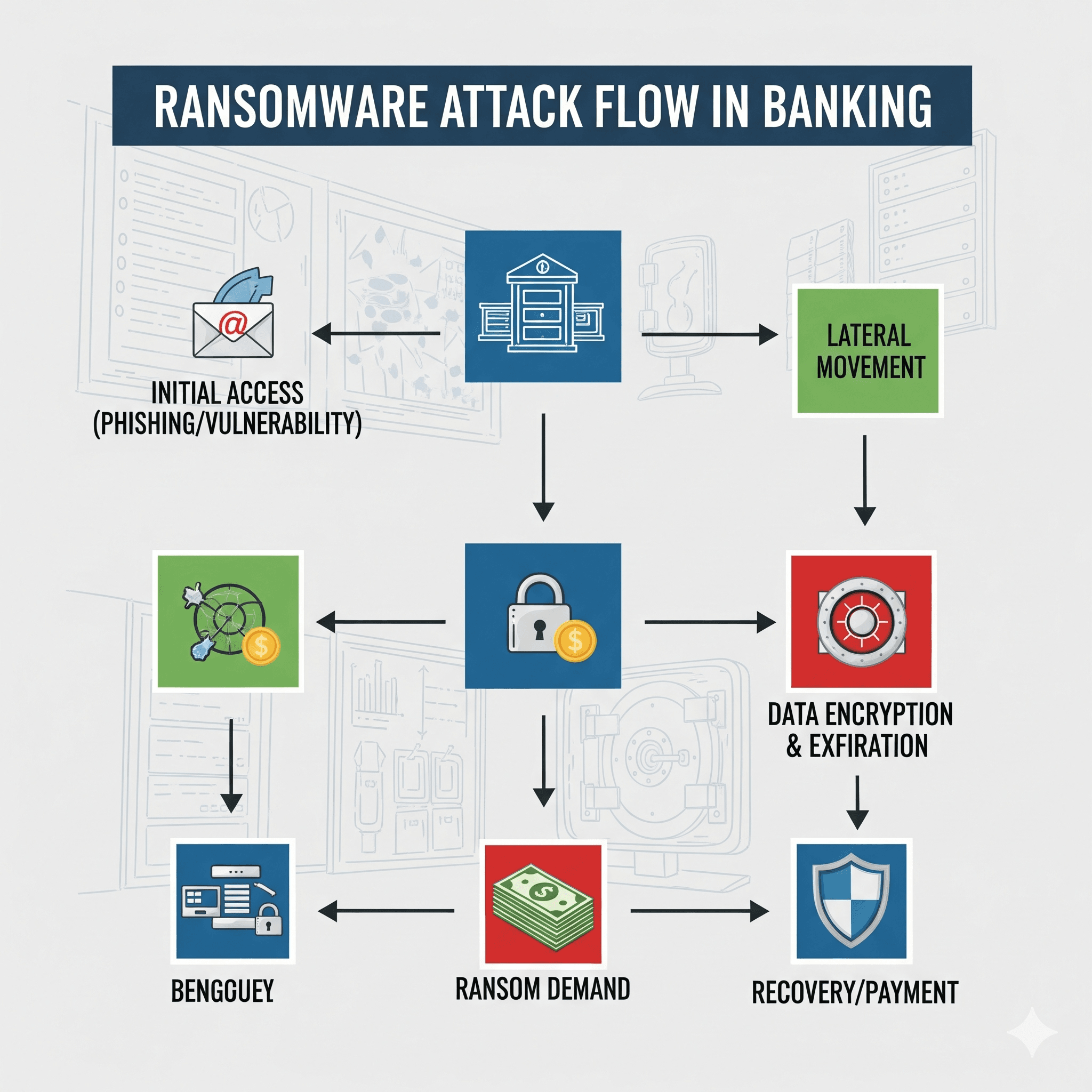
| Ransomware Type | Target Systems | Impact Level | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banking Trojans | Core banking systems, ATM networks | Critical | 2-4 weeks |
| Payment System Attacks | SWIFT gateways, Payment processors | Severe | 1-3 weeks |
| Data Encryption | Customer databases, Transaction logs | High | 3-7 days |
| Infrastructure Attacks | Network systems, Backup servers | Critical | 1-2 weeks |
Challenge #3: API Security Vulnerabilities and Third-Party Risks
The rise of embedded finance and open banking has exponentially increased API usage, creating new attack vectors. Broken authentication, improper access controls, and exposed endpoints are becoming major security concerns.
API Security Facts
Financial services rank among the top 3 industries targeted by API attacks. The embedded finance market is projected to reach $251.5 billion by 2029, significantly expanding the attack surface.
- Broken Object Level Authorization (BOLA): Attackers manipulate object IDs to access unauthorized data
- Broken Authentication: Weak implementation of authentication mechanisms in APIs
- Excessive Data Exposure: APIs returning more data than necessary to function
- Rate Limiting Issues: Lack of proper controls leading to DDoS and brute force attacks
- Improper Asset Management: Shadow APIs and outdated versions creating security gaps
// Secure API endpoint with rate limiting and authentication
const express = require('express');
const rateLimit = require('express-rate-limit');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const helmet = require('helmet');
const app = express();
// Security middleware
app.use(helmet());
// Rate limiting
const apiLimiter = rateLimit({
windowMs: 15 * 60 * 1000, // 15 minutes
max: 100, // limit each IP to 100 requests per windowMs
message: 'Too many requests from this IP'
});
app.use('/api/', apiLimiter);
// JWT verification middleware
const verifyToken = (req, res, next) => {
const token = req.headers['authorization']?.split(' ');
if (!token) {
return res.status(401).json({ error: 'Access denied' });
}
try {
const verified = jwt.verify(token, process.env.JWT_SECRET);
req.user = verified;
next();
} catch (error) {
res.status(400).json({ error: 'Invalid token' });
}
};
// Secure endpoint
app.get('/api/account-balance', verifyToken, (req, res) => {
// Implementation with proper authorization checks
const userId = req.user.id;
// Verify user can access this specific account
res.json({ balance: getAccountBalance(userId) });
});Cybercriminals are leveraging artificial intelligence to create more sophisticated and convincing attacks. AI-powered phishing, deepfake fraud, and adaptive malware are becoming increasingly difficult to detect and defend against.
- AI-Generated Phishing: Highly personalized emails that bypass traditional filters
- Deepfake Voice Fraud: Synthetic audio mimicking executives to authorize fraudulent transfers
- Adaptive Malware: Self-modifying code that evades signature-based detection
- Automated Social Engineering: AI chatbots conducting large-scale social engineering campaigns
"The weaponization of AI in cybercrime represents a paradigm shift. Financial institutions must adopt AI-powered defense systems to match the sophistication of modern threats."
— Cybersecurity Expert, BreachLock
Challenge #5: Cloud Security and Hybrid Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
As 84% of financial institutions report cloud computing as critical to their business, securing hybrid and multi-cloud environments has become a top priority. Misconfigurations, inadequate access controls, and poor visibility across cloud platforms create significant security gaps.
Cloud Security Reality
Organizations experiencing cloud security incidents jumped from 24% to 61% in 2024. Poor configurations and inadequate monitoring are the primary culprits.
Strategic Mitigation Approaches
Financial institutions must adopt a comprehensive, multi-layered security approach that combines advanced technology, rigorous processes, and continuous monitoring to address these evolving threats.
| Security Control | Implementation | Effectiveness | Investment Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Trust Architecture | Identity verification for every access request | High | Moderate |
| AI-Powered SIEM | Machine learning for threat detection | Very High | High |
| Immutable Backups | Air-gapped, tamper-proof data storage | High | Low |
| Regular Penetration Testing | Quarterly security assessments | High | Moderate |
| Employee Security Training | Continuous awareness programs | Moderate | Low |
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
New regulations like DORA in the EU and enhanced SEC cyber disclosure rules in the US require financial institutions to maintain robust cybersecurity frameworks with continuous monitoring, incident reporting, and board-level oversight.
Best Practice Recommendation
Implement a risk-based cybersecurity framework that aligns with business objectives, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices. Regular testing and updates are essential for maintaining effectiveness.
Looking Ahead: Future Security Considerations
As quantum computing advances, financial institutions must prepare for quantum-resistant encryption. Post-quantum cryptography standards are being developed to protect against future quantum-based attacks that could compromise current encryption methods.
Conclusion
The cybersecurity challenges facing financial institutions in 2025 are complex and evolving rapidly. Success requires a proactive approach combining advanced technology, skilled personnel, robust processes, and strong regulatory compliance. Organizations that invest in comprehensive cybersecurity strategies today will be better positioned to protect their customers and maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly digital financial landscape.
Reading Progress
0% completed
Article Insights
Share Article
Quick Actions
Stay Updated
Join 12k+ readers worldwide
Get the latest insights, tutorials, and industry news delivered straight to your inbox. No spam, just quality content.
Unsubscribe at any time. No spam, ever. 🚀
