Mastering Data Visualization for Actionable Insights
Discover how to create compelling data visualizations that transform complex datasets into clear, actionable insights that drive informed decision-making and business success across all organizational levels.
Introduction
Understanding the Strategic Value of Data Visualization
Data visualization serves as a critical bridge between complex analytical findings and actionable business insights by transforming abstract numbers into clear patterns that inform decisions, guide policy, and shape organizational understanding. Modern visualization goes beyond simple chart creation to encompass strategic communication that enables stakeholders at all levels to quickly grasp key messages, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions based on data-driven evidence. The strategic value lies in visualization's ability to reveal insights that would be difficult or impossible to detect in raw data formats, enabling organizations to spot trends, identify anomalies, and understand relationships that drive business performance.

Business Impact
Organizations that master data visualization achieve faster decision-making, improved strategic alignment, and enhanced ability to communicate insights across technical and non-technical audiences, leading to measurable improvements in business outcomes.
- Pattern Recognition: Visual representations enable immediate identification of trends, correlations, and anomalies that might be missed in numerical formats
- Decision Acceleration: Clear visualizations reduce time required for data interpretation and enable faster, more confident decision-making
- Stakeholder Engagement: Compelling visuals capture attention and foster deeper understanding across diverse audiences and expertise levels
- Insight Communication: Effective visualization translates complex analytical findings into accessible narratives that drive action
- Business Alignment: Visual storytelling helps align teams around shared understanding of data-driven insights and strategic priorities
Selecting Appropriate Visualization Types
Choosing the right visualization type is fundamental to effective data communication, with different chart types serving specific purposes based on the underlying data structure and the story being told. Line charts excel at showing trends over time, bar charts provide clear comparisons between categories, pie charts illustrate proportions of a whole, scatter plots reveal relationships between variables, and heatmaps effectively display patterns and density across multiple dimensions. The key to successful visualization selection lies in understanding your audience's needs, the data's characteristics, and the specific insights you want to communicate.
| Visualization Type | Best Use Cases | Data Requirements | Audience Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line Charts | Trends over time, continuous data analysis | Time series data with continuous values | Technical and non-technical audiences familiar with temporal analysis |
| Bar Charts | Category comparisons, ranking analysis | Categorical data with quantitative measures | Universal understanding, suitable for all audience levels |
| Scatter Plots | Correlation analysis, relationship exploration | Two or more continuous variables | Analytical audiences comfortable with statistical concepts |
| Heatmaps | Pattern visualization, density analysis, correlation matrices | Multi-dimensional data with numeric values | Data-savvy audiences who can interpret color-coded information |
Design Principles for Clear Communication
Effective data visualization design prioritizes clarity and simplicity over decoration, ensuring that visual elements serve the primary purpose of communicating insights rather than creating aesthetic appeal. Key design principles include maintaining focus on the data story, using consistent color schemes that enhance rather than distract from key messages, providing clear labels and annotations, and eliminating unnecessary visual elements that can clutter or confuse the viewer. The goal is to create visualizations that allow viewers to immediately understand the key insights without requiring extensive explanation or interpretation.
Design Excellence
The most effective visualizations achieve maximum insight communication with minimum cognitive effort, enabling viewers to quickly understand key messages and take appropriate action based on the presented data.
Data Preparation and Quality Assurance
High-quality data visualization begins with thorough data preparation and quality assurance processes that ensure accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the underlying information being visualized. Data cleaning involves identifying and addressing missing values, removing duplicates, standardizing formats, and validating data integrity to prevent misleading visualizations that could lead to incorrect business decisions. Proper data preparation also includes understanding data context, identifying potential biases or limitations, and ensuring that visualization choices appropriately represent the underlying data characteristics.

Color Theory and Visual Hierarchy
Strategic use of color and visual hierarchy guides viewer attention to key insights while ensuring accessibility and clarity across diverse audiences and viewing conditions. Color selection should consider both aesthetic appeal and functional purpose, using contrasting colors to highlight important comparisons, consistent color schemes to maintain visual coherence, and colorblind-friendly palettes to ensure inclusivity. Visual hierarchy techniques including size variation, positioning, and contrast help direct viewer attention to the most important elements while supporting secondary information through subtle visual cues.
- Functional Color Usage: Colors should serve specific purposes such as highlighting key data points, indicating categories, or showing progression rather than purely decorative purposes
- Accessibility Considerations: Color palettes must be accessible to colorblind viewers and provide sufficient contrast for various viewing conditions and devices
- Consistency Standards: Maintaining consistent color usage across related visualizations helps viewers develop familiarity and reduces cognitive load
- Cultural Sensitivity: Color choices should consider cultural associations and business context to avoid unintended messaging or confusion
- Visual Balance: Effective color distribution creates visual balance that supports comprehension without overwhelming or distracting from key insights
Interactive Elements and User Experience
Interactive visualizations transform static data presentations into dynamic experiences that allow users to explore information at their own pace, uncovering insights through personalized investigation and drill-down capabilities. Effective interactive elements include filters that enable focused analysis, hover effects that provide additional context, drill-down functionality that reveals underlying details, and dynamic controls that allow users to adjust parameters and view different perspectives. The key to successful interactivity is ensuring that interactive features enhance rather than complicate the user experience, providing intuitive controls that support exploration without overwhelming users with excessive options.
Storytelling Through Data Visualization
Data storytelling transforms visualization from simple information display into compelling narratives that guide viewers through logical sequences from context to insights to recommended actions. Effective data stories begin with establishing context and background, progress through evidence presentation and analysis, highlight key findings and implications, and conclude with clear recommendations or next steps. The narrative structure helps viewers understand not just what the data shows, but why it matters and what actions should be taken based on the insights revealed.
Narrative Impact
Data visualizations that follow clear narrative structures are significantly more effective at driving action and decision-making compared to standalone charts or graphs without contextual storytelling.
Real-Time and Dynamic Visualization Techniques
Real-time data visualization enables organizations to monitor changing conditions, respond quickly to emerging trends, and make timely decisions based on current rather than historical information. Dynamic visualization techniques include live dashboards that update automatically with new data, streaming analytics displays that show evolving patterns, and alert systems that highlight significant changes or threshold breaches. Successful real-time visualization balances the need for current information with system performance considerations, ensuring that updates are meaningful and actionable rather than simply frequent.
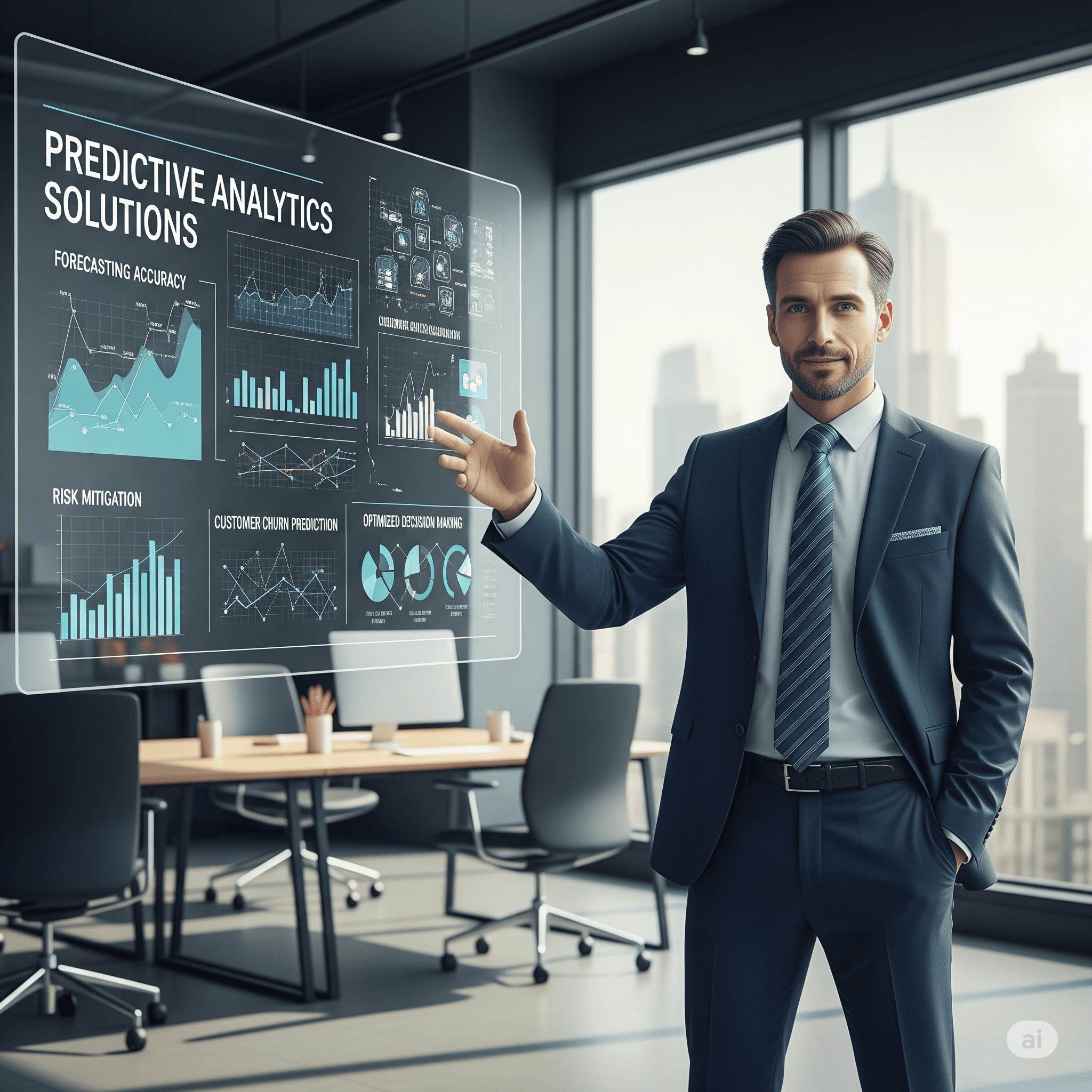

Advanced Visualization Techniques
Advanced visualization techniques including geospatial mapping, network analysis, and multidimensional displays enable analysis of complex datasets that cannot be effectively represented through traditional chart types. Geospatial visualizations reveal location-based patterns and relationships critical for logistics, marketing, and operations analysis, while network diagrams show relationships and connections between entities. Three-dimensional and multidimensional techniques can reveal patterns in complex datasets, though they require careful implementation to avoid confusion or misinterpretation.
Tools and Technology Selection
Selecting appropriate visualization tools requires balancing technical capabilities, user skill levels, integration requirements, and cost considerations to find solutions that meet specific organizational needs. Popular tools including Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js offer different strengths, with Tableau providing user-friendly drag-and-drop interfaces, Power BI offering strong Microsoft ecosystem integration, and D3.js enabling highly customized web-based visualizations for technically sophisticated users. The choice depends on factors including data sources, technical expertise, customization requirements, collaboration needs, and budget constraints.
| Tool Category | Representative Tools | Best Use Cases | Skill Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Platforms | Tableau, Power BI, Qlik Sense | Business intelligence, departmental analytics, executive dashboards | Moderate technical skills, business domain knowledge |
| Programming Libraries | D3.js, Python matplotlib, R ggplot2 | Custom visualizations, statistical analysis, research applications | Strong programming skills, statistical knowledge |
| Cloud-Based Solutions | Google Data Studio, Amazon QuickSight, Looker | Collaborative analytics, scalable deployment, cost-effective solutions | Moderate technical skills, cloud platform familiarity |
| Specialized Tools | Gephi (networks), QGIS (geospatial), Plotly (interactive) | Domain-specific visualization needs, specialized analysis types | Domain expertise, specialized technical knowledge |
Mobile and Cross-Platform Considerations
Modern data visualization must account for diverse viewing platforms including desktop computers, tablets, and mobile devices, requiring responsive design approaches that maintain clarity and functionality across different screen sizes and interaction methods. Mobile-optimized visualizations prioritize essential information, use larger touch targets, and adapt layouts to accommodate smaller screens while preserving key insights and interactive capabilities. Cross-platform consistency ensures that visualizations provide equivalent experiences regardless of viewing device, supporting both technical and business user needs.
Accessibility and Inclusive Design
Accessible data visualization design ensures that insights are available to all users regardless of visual capabilities, technical expertise, or assistive technology requirements. Accessibility considerations include providing alternative text descriptions, using sufficient color contrast, offering multiple ways to access information, and designing visualizations that work with screen readers and other assistive technologies. Inclusive design principles extend beyond disability accommodations to consider diverse user needs, cultural contexts, and varying levels of data literacy.
Inclusive Impact
Accessible visualization design not only serves users with specific needs but often improves the overall user experience for all viewers by promoting clarity, simplicity, and multiple information pathways.
Performance and Scalability Optimization
Large-scale data visualization requires careful attention to performance optimization and scalability considerations that ensure responsive user experiences even with extensive datasets. Optimization techniques include data aggregation and sampling for overview displays, progressive loading for detailed views, efficient rendering algorithms, and caching strategies that balance data freshness with system responsiveness. Scalability planning considers both data volume growth and user adoption increases, ensuring that visualization solutions can evolve with organizational needs.
Integration with Business Intelligence Systems
Effective data visualization requires seamless integration with existing business intelligence infrastructure, data warehouses, and analytical workflows to provide consistent and reliable information for decision-making. Integration considerations include data connectivity and refresh mechanisms, user authentication and security, consistency with existing reporting systems, and alignment with established data governance policies. Successful integration enables visualization to complement rather than compete with existing analytical tools and processes.
Quality Assurance and Validation Processes
Systematic quality assurance processes ensure that visualizations accurately represent underlying data and effectively communicate intended insights without introducing errors or misinterpretations. Validation procedures include data accuracy verification, visual design review, user testing with target audiences, and performance assessment under realistic usage conditions. Regular quality reviews help identify and address issues including data inconsistencies, visual ambiguities, and usability problems that could undermine visualization effectiveness.
- Data Accuracy Verification: Systematic checking of calculations, aggregations, and transformations to ensure mathematical correctness
- Visual Design Review: Assessment of color choices, layout decisions, and interactive elements for clarity and effectiveness
- User Experience Testing: Evaluation with representative users to identify usability issues and comprehension problems
- Performance Validation: Testing under realistic data volumes and user loads to ensure acceptable response times
- Accessibility Compliance: Verification that visualizations meet accessibility standards and work with assistive technologies
Measuring Impact and Effectiveness
Measuring the impact and effectiveness of data visualization initiatives requires establishing clear metrics that assess both technical performance and business value outcomes. Key performance indicators include user engagement metrics such as time spent with visualizations and frequency of use, decision-making improvements measured through faster response times and better outcomes, and business impact demonstrated through measurable improvements in key performance areas. Regular assessment helps optimize visualization strategies and demonstrate return on investment for visualization initiatives.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
The future of data visualization is being shaped by emerging technologies including artificial intelligence for automated insight discovery, augmented reality for immersive data exploration, natural language interfaces for query-based visualization, and machine learning for personalized visualization experiences. AI-driven platforms can automatically detect patterns, trends, and anomalies while generating appropriate visualizations and narrative explanations, reducing the technical barrier for creating effective data communications. These advances promise to make sophisticated visualization capabilities accessible to broader audiences while enabling more intuitive and powerful ways to explore and understand complex data.
Building Organizational Visualization Capabilities
Developing organizational data visualization capabilities requires strategic investment in tools, training, and processes that enable widespread adoption and effective use across different roles and departments. Capability building includes establishing visualization standards and guidelines, providing training programs for different skill levels, creating communities of practice for knowledge sharing, and developing governance frameworks that ensure quality and consistency. Successful organizations treat visualization as a core competency that supports data-driven decision-making throughout the organization.
| Capability Area | Development Strategies | Success Metrics | Organizational Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical Skills | Training programs, tool certification, hands-on workshops | User proficiency scores, tool adoption rates, visualization quality | Increased self-service analytics, reduced dependency on specialists |
| Design Competency | Design thinking workshops, best practice sharing, style guides | Visual effectiveness ratings, user comprehension scores | Improved communication clarity, better decision-making support |
| Strategic Alignment | Business case development, executive sponsorship, governance frameworks | Business value measurement, strategic project integration | Enhanced data-driven culture, competitive advantage |
| Innovation Culture | Experimentation programs, technology evaluation, knowledge sharing | New technique adoption, innovative solution development | Continuous improvement, technological leadership |
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Understanding and avoiding common visualization mistakes is essential for creating effective data communications that support rather than hinder decision-making processes. Frequent pitfalls include choosing inappropriate chart types for the data structure, overcomplicated designs that obscure key insights, misleading scales or representations that distort data interpretation, and failure to consider audience needs and technical capabilities. Prevention strategies include following established design principles, conducting user testing, seeking feedback from diverse audiences, and maintaining focus on communication objectives rather than visual aesthetics.
Pitfall Prevention
The most effective way to avoid visualization pitfalls is through systematic design review processes that evaluate both technical accuracy and communication effectiveness before deployment.
Conclusion
Mastering data visualization for actionable insights represents a critical capability for organizations seeking to leverage data as a strategic asset in increasingly complex and competitive business environments. Effective visualization goes beyond creating attractive charts to encompass strategic communication that transforms complex datasets into clear narratives that drive informed decision-making across all organizational levels. Success requires combining technical proficiency with design excellence, audience understanding, and business acumen to create visual communications that not only inform but also inspire action and drive measurable business outcomes. As data volumes continue to grow and business environments become more dynamic, organizations that invest in visualization capabilities will gain significant advantages through faster decision-making, improved strategic alignment, and enhanced ability to communicate insights across diverse stakeholders. The future belongs to organizations that can effectively bridge the gap between data and decision-making through compelling visual storytelling that transforms information into intelligence and intelligence into action.
Reading Progress
0% completed
Article Insights
Share Article
Quick Actions
Stay Updated
Join 12k+ readers worldwide
Get the latest insights, tutorials, and industry news delivered straight to your inbox. No spam, just quality content.
Unsubscribe at any time. No spam, ever. 🚀
