Native vs Cross-Platform: Choosing the Right Approach
Explore the pros and cons of native and cross-platform development to make informed decisions.

Introduction
Understanding Development Approaches
Native development involves creating platform-specific applications using languages and tools designed for each operating system, while cross-platform development enables building apps that run on multiple platforms from a single codebase.
Market Reality
Cross-platform development can reduce development costs by 30-40% while native apps typically deliver 20-30% better performance in resource-intensive applications.
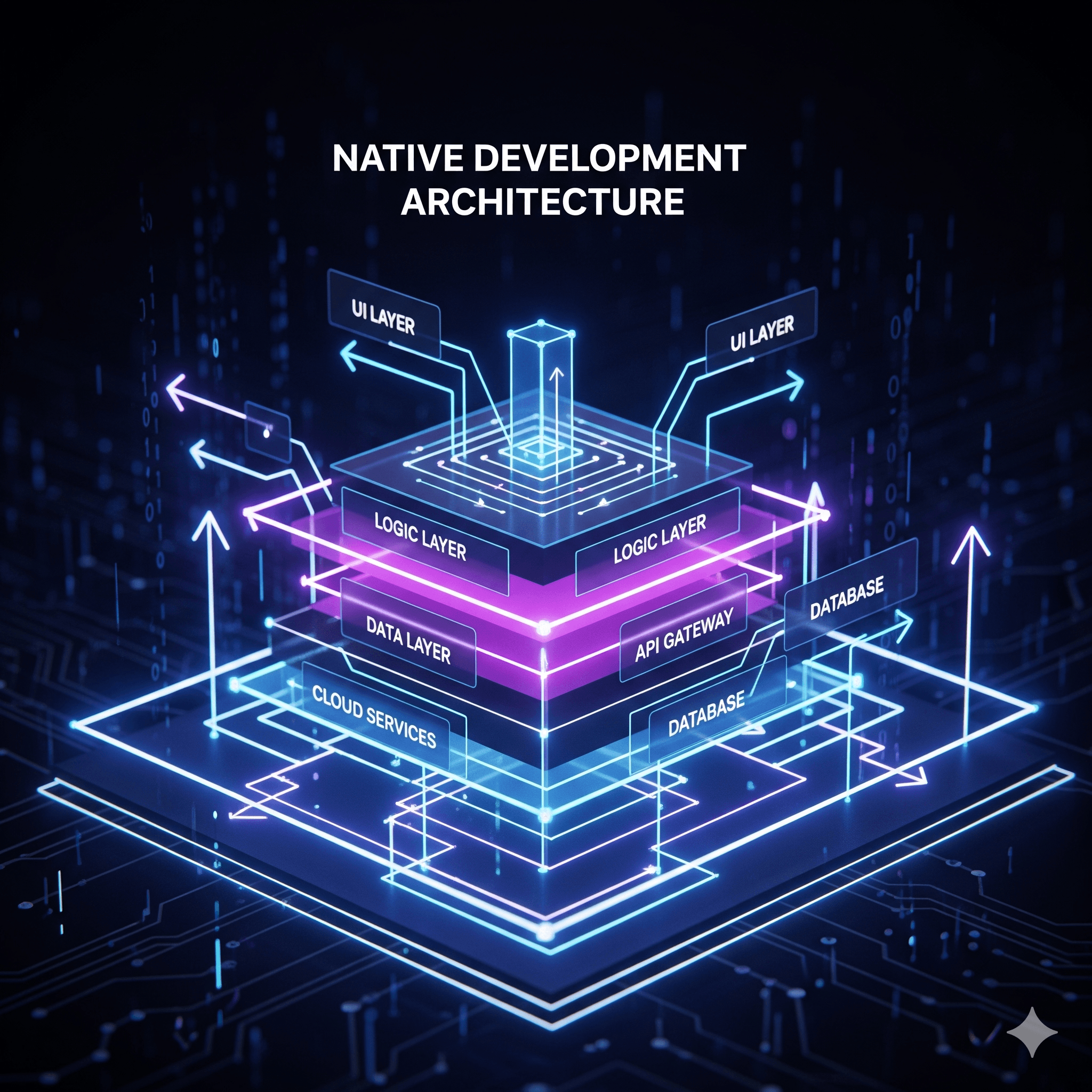
Native Development Overview
Native development leverages platform-specific technologies to create applications that fully utilize device capabilities and provide optimal user experience through platform-native UI components.
| Platform | Languages | IDE | Key Frameworks |
|---|---|---|---|
| iOS | Swift, Objective-C | Xcode | UIKit, SwiftUI, Core Data |
| Android | Java, Kotlin | Android Studio | Android SDK, Jetpack Compose |
| Windows | C#, C++ | Visual Studio | .NET, WinUI, UWP |
| macOS | Swift, Objective-C | Xcode | AppKit, SwiftUI |
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var userInput = ""
@State private var items: [String] = []
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
VStack {
HStack {
TextField("Enter item", text: $userInput)
.textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle())
Button("Add") {
if !userInput.isEmpty {
items.append(userInput)
userInput = ""
}
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
}
.padding()
List {
ForEach(items, id: \.self) { item in
Text(item)
}
.onDelete(perform: deleteItems)
}
}
.navigationTitle("Native iOS App")
}
}
func deleteItems(offsets: IndexSet) {
items.remove(atOffsets: offsets)
}
}
Cross-Platform Development Landscape
Cross-platform frameworks enable developers to write code once and deploy across multiple platforms, offering significant time and cost savings while maintaining reasonable performance.
| Framework | Language | Performance | UI Approach | Popularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| React Native | JavaScript/TypeScript | Good | Native components | Very High |
| Flutter | Dart | Excellent | Custom rendering | High |
| Xamarin | C# | Good | Native components | Medium |
| Ionic | HTML/CSS/JS | Fair | WebView | Medium |
| Cordova/PhoneGap | HTML/CSS/JS | Fair | WebView | Declining |
React Native Implementation
React Native bridges JavaScript and native components, enabling developers familiar with React to build mobile apps while accessing native device features.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import {
View,
Text,
TextInput,
TouchableOpacity,
FlatList,
StyleSheet,
Alert,
} from 'react-native';
import AsyncStorage from '@react-native-async-storage/async-storage';
const TodoApp = () => {
const [task, setTask] = useState('');
const [tasks, setTasks] = useState([]);
useEffect(() => {
loadTasks();
}, []);
const loadTasks = async () => {
try {
const savedTasks = await AsyncStorage.getItem('tasks');
if (savedTasks) {
setTasks(JSON.parse(savedTasks));
}
} catch (error) {
Alert.alert('Error', 'Failed to load tasks');
}
};
const saveTasks = async (newTasks) => {
try {
await AsyncStorage.setItem('tasks', JSON.stringify(newTasks));
} catch (error) {
Alert.alert('Error', 'Failed to save tasks');
}
};
const addTask = () => {
if (task.trim()) {
const newTasks = [...tasks, { id: Date.now(), text: task }];
setTasks(newTasks);
saveTasks(newTasks);
setTask('');
}
};
const deleteTask = (id) => {
const newTasks = tasks.filter(item => item.id !== id);
setTasks(newTasks);
saveTasks(newTasks);
};
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.title}>Cross-Platform Todo</Text>
<View style={styles.inputContainer}>
<TextInput
style={styles.input}
value={task}
onChangeText={setTask}
placeholder="Enter a task"
/>
<TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={addTask}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>Add</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<FlatList
data={tasks}
keyExtractor={(item) => item.id.toString()}
renderItem={({ item }) => (
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.taskItem}
onLongPress={() => deleteTask(item.id)}
>
<Text style={styles.taskText}>{item.text}</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
)}
/>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
backgroundColor: '#f5f5f5',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
marginBottom: 20,
textAlign: 'center',
},
inputContainer: {
flexDirection: 'row',
marginBottom: 20,
},
input: {
flex: 1,
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: '#ddd',
padding: 10,
borderRadius: 5,
backgroundColor: 'white',
},
button: {
backgroundColor: '#007AFF',
padding: 10,
borderRadius: 5,
marginLeft: 10,
},
buttonText: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
taskItem: {
backgroundColor: 'white',
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 5,
marginBottom: 10,
},
taskText: {
fontSize: 16,
},
});
export default TodoApp;Flutter Development Approach
Flutter uses its own rendering engine to create pixel-perfect UIs that look identical across platforms while providing near-native performance through Dart's compilation to native code.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:shared_preferences/shared_preferences.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
visualDensity: VisualDensity.adaptivePlatformDensity,
),
home: TodoScreen(),
);
}
}
class TodoScreen extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_TodoScreenState createState() => _TodoScreenState();
}
class _TodoScreenState extends State<TodoScreen> {
final TextEditingController _controller = TextEditingController();
List<String> _tasks = [];
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_loadTasks();
}
_loadTasks() async {
SharedPreferences prefs = await SharedPreferences.getInstance();
setState(() {
_tasks = prefs.getStringList('tasks') ?? [];
});
}
_saveTasks() async {
SharedPreferences prefs = await SharedPreferences.getInstance();
prefs.setStringList('tasks', _tasks);
}
_addTask() {
if (_controller.text.isNotEmpty) {
setState(() {
_tasks.add(_controller.text);
_controller.clear();
});
_saveTasks();
}
}
_deleteTask(int index) {
setState(() {
_tasks.removeAt(index);
});
_saveTasks();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter Todo App'),
elevation: 0,
),
body: Column(
children: [
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
child: Row(
children: [
Expanded(
child: TextField(
controller: _controller,
decoration: InputDecoration(
hintText: 'Enter a task',
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
),
),
),
SizedBox(width: 10),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _addTask,
child: Text('Add'),
),
],
),
),
Expanded(
child: ListView.builder(
itemCount: _tasks.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return Card(
margin: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16, vertical: 4),
child: ListTile(
title: Text(_tasks[index]),
trailing: IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.delete, color: Colors.red),
onPressed: () => _deleteTask(index),
),
),
);
},
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
Decision Matrix and Considerations
Choosing between native and cross-platform development requires evaluating multiple factors including project requirements, team expertise, timeline, and long-term maintenance considerations.
| Factor | Native | Cross-Platform | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent | Good to Very Good | Native |
| Development Speed | Slower | Faster | Cross-Platform |
| Code Reusability | 0% | 60-90% | Cross-Platform |
| Platform Features | Full Access | Limited/Delayed | Native |
| UI Consistency | Platform Native | Uniform/Custom | Depends |
| Team Expertise | Platform Specific | Unified Skillset | Cross-Platform |
| Maintenance | Separate Codebases | Single Codebase | Cross-Platform |
| App Store Approval | Standard | Standard | Tie |
Performance Consideration
While cross-platform performance has improved significantly, CPU-intensive applications like games, AR/VR apps, or real-time processing may still benefit from native development.
When to Choose Native Development
- Performance Critical Applications: Games, AR/VR, or real-time processing apps
- Platform-Specific Features: Heavy use of latest platform APIs or hardware
- Complex UI Requirements: Highly customized or platform-specific interfaces
- Long-term Investment: Apps with extended lifecycle and platform optimization needs
- Existing Native Expertise: Teams already skilled in platform-specific development
When to Choose Cross-Platform
- MVP Development: Quick time-to-market with limited resources
- Standard Business Apps: CRUD operations, forms, and basic functionality
- Unified Design: Consistent look and feel across all platforms
- Small Development Teams: Limited resources for maintaining multiple codebases
- Budget Constraints: Cost optimization is a primary concern
"The best technology choice is not the most advanced one, but the one that best fits your project requirements, team capabilities, and business objectives."
— Software Architecture Principle
Hybrid Approaches and Future Trends
Modern development often employs hybrid strategies, combining cross-platform foundations with native modules for platform-specific features, offering the best of both approaches.
Emerging Trend
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are becoming a viable third option, offering app-like experiences through web technologies with native capabilities.
// React Native bridge to native iOS module
import { NativeModules, Platform } from 'react-native';
const { BiometricAuth } = NativeModules;
class AuthService {
static async authenticateWithBiometric() {
try {
if (Platform.OS === 'ios') {
const result = await BiometricAuth.authenticateWithTouchID({
reason: 'Authenticate to access your account',
fallbackLabel: 'Use Passcode'
});
return result;
} else {
// Android implementation
const result = await BiometricAuth.authenticateWithFingerprint();
return result;
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('Biometric authentication failed:', error);
throw error;
}
}
static async checkBiometricAvailability() {
return await BiometricAuth.isHardwareAvailable();
}
}
export default AuthService;Cost-Benefit Analysis Framework
Implementing a systematic evaluation framework helps make objective decisions based on quantifiable factors rather than technology preferences.
| Evaluation Criteria | Weight | Native Score | Cross-Platform Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Development Time | 25% | 6/10 | 9/10 |
| Performance Requirements | 20% | 10/10 | 7/10 |
| Team Expertise | 15% | 7/10 | 8/10 |
| Maintenance Complexity | 15% | 6/10 | 9/10 |
| Feature Requirements | 10% | 9/10 | 7/10 |
| Budget Constraints | 10% | 5/10 | 9/10 |
| Time to Market | 5% | 6/10 | 9/10 |

Conclusion
The choice between native and cross-platform development depends on your specific project requirements, team capabilities, and business objectives. Modern cross-platform frameworks have significantly closed the performance gap while offering substantial development efficiency gains. Consider your long-term strategy, maintenance requirements, and user experience expectations when making this crucial architectural decision.
Reading Progress
0% completed
Article Insights
Share Article
Quick Actions
Stay Updated
Join 12k+ readers worldwide
Get the latest insights, tutorials, and industry news delivered straight to your inbox. No spam, just quality content.
Unsubscribe at any time. No spam, ever. 🚀
