SQL vs NoSQL: Choosing the Right Database
Understand the key differences and use cases for SQL and NoSQL databases to make informed decisions.
Introduction
Understanding SQL Databases
SQL (Structured Query Language) databases, also known as relational databases, organize data in structured tables with predefined schemas. They follow ACID properties and use SQL for querying, making them ideal for applications requiring data consistency and complex relationships.
ACID Properties
Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability ensure reliable transaction processing in SQL databases, making them perfect for financial and enterprise applications.
Key Characteristics of SQL Databases
- Structured Schema: Predefined table structure with fixed columns and data types.
- ACID Compliance: Ensures data integrity through reliable transaction processing.
- Complex Queries: Supports sophisticated JOIN operations and analytical queries.
- Vertical Scaling: Primarily scales by increasing server hardware capacity.
- Mature Ecosystem: Extensive tooling, documentation, and developer expertise.
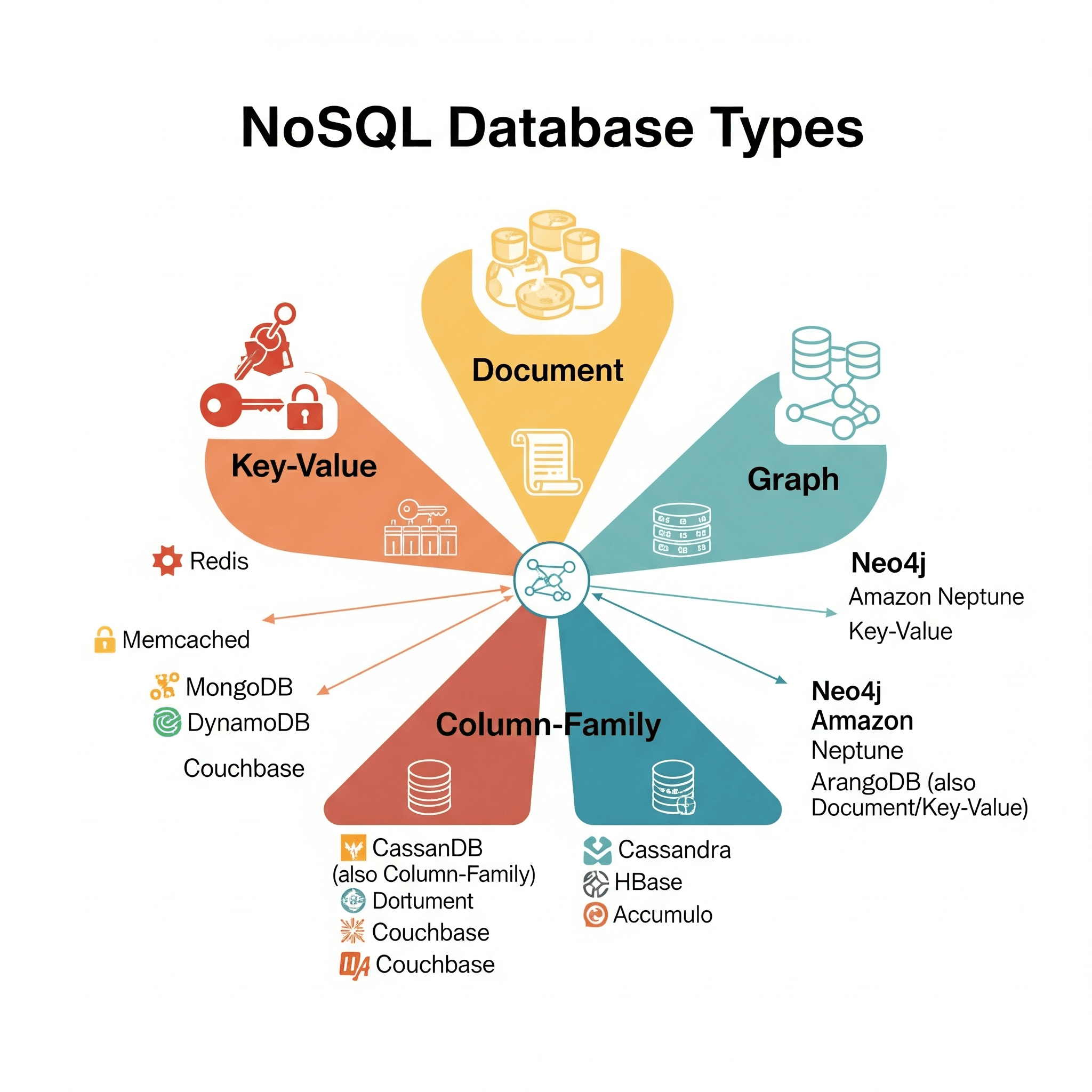
Exploring NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases embrace flexible, schema-less designs optimized for specific data models and use cases. They prioritize horizontal scalability, performance, and developer agility over strict consistency requirements.
Types of NoSQL Databases
- Document Stores: MongoDB, CouchDB - Store data as JSON-like documents.
- Key-Value Stores: Redis, DynamoDB - Simple key-value pair storage.
- Column-Family: Cassandra, HBase - Organize data in column families.
- Graph Databases: Neo4j, Amazon Neptune - Optimized for relationship data.
Comprehensive Comparison
| Aspect | SQL Databases | NoSQL Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Schema | Fixed, predefined structure | Flexible, schema-less or schema-on-read |
| Scalability | Vertical scaling (scale-up) | Horizontal scaling (scale-out) |
| Consistency | Strong consistency (ACID) | Eventual consistency (BASE) |
| Query Language | Standardized SQL | Database-specific APIs |
| Data Relationships | Complex joins supported | Limited join capabilities |
| Performance | Optimized for complex queries | Optimized for simple operations |
| Use Cases | Financial, ERP, CRM systems | Web apps, IoT, real-time analytics |
-- Complex join query in SQL
SELECT u.name, p.title, c.comment_text
FROM users u
JOIN posts p ON u.id = p.user_id
JOIN comments c ON p.id = c.post_id
WHERE u.active = true
ORDER BY p.created_at DESC;// Document-based query in MongoDB
db.posts.aggregate([
{
$lookup: {
from: "users",
localField: "user_id",
foreignField: "_id",
as: "user"
}
},
{
$match: { "user.active": true }
},
{
$sort: { "created_at": -1 }
}
]);When to Choose SQL
SQL databases excel in scenarios requiring data integrity, complex relationships, and analytical capabilities. They're the preferred choice for traditional business applications and systems with well-defined requirements.
- Applications requiring strict data consistency and ACID transactions.
- Complex analytical queries and reporting requirements.
- Well-established data relationships and normalized structures.
- Regulatory compliance and audit requirements.
- Teams with strong SQL expertise and existing SQL infrastructure.
When to Choose NoSQL
NoSQL databases shine in modern applications requiring rapid scaling, flexible data models, and high-performance operations. They're ideal for startups and applications with evolving requirements.
- Rapid scaling requirements with unpredictable traffic patterns.
- Flexible or evolving data schemas and structures.
- Real-time applications with low-latency requirements.
- Big data and analytics workloads with simple query patterns.
- Microservices architectures requiring database per service.
Hybrid Approach
Many modern applications use both SQL and NoSQL databases in a polyglot persistence approach, choosing the right database for each specific use case within the same system.
Popular Database Examples
Understanding specific implementations helps in making practical decisions for your technology stack.
| SQL Databases | NoSQL Databases | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| PostgreSQL | MongoDB | General-purpose applications |
| MySQL | Redis | Web applications with caching |
| Oracle | Cassandra | Enterprise and big data |
| SQL Server | Neo4j | Business intelligence and graphs |
| SQLite | DynamoDB | Mobile and serverless applications |
"The best database is not the one with the most features, but the one that best fits your specific use case, team expertise, and long-term requirements."
— Database Architecture Expert
Decision Framework
Making the right database choice requires evaluating multiple factors including data structure, scalability needs, consistency requirements, and team capabilities.
Key Takeaway
There's no universal winner between SQL and NoSQL. The right choice depends on your specific requirements, data patterns, scalability needs, and team expertise.
Conclusion
Both SQL and NoSQL databases have their place in modern architecture. SQL databases provide reliability and complex querying capabilities, while NoSQL databases offer flexibility and scalability. Understanding their strengths helps architects build robust, efficient systems that can evolve with changing requirements.
Reading Progress
0% completed
Article Insights
Share Article
Quick Actions
Stay Updated
Join 12k+ readers worldwide
Get the latest insights, tutorials, and industry news delivered straight to your inbox. No spam, just quality content.
Unsubscribe at any time. No spam, ever. 🚀
